content of level
Works of Hanbli school
Al-Marawi’s Al-Inf. Ibn Mufli’s Al-Fur, and those by later scholars include Mansour al-Bahuti’s - Kashf al-Qina'an Matn al-Iqna'
Hanbli school
Methodology: Texts, The rulings of the Prophet’s Companions, whenever they agreed on a question. When the Prophet’s Companions disagreed, he would choose the view he considered closest to the Qur’an and the Sunnah.
works of Al-Shafi'i School
Mohammed al-Ramli -Nihayat al-Muhtaj ila Shar al-Minhaj; 2) Ahmad al-Haytami’s -Tufaht al-Muhtaj fi Sharh al-Minhaj; and 3) al-Khab al-Shirbni’s Mughni- al-Muhtaj ila Shar al-Minhaj.
Al-Shafi'i School
Methodology: Qur'an, Sunnah, Unanimity of (all) the Scholars, the statement of any Companion of the Prophet (pbuh), provided there is no disagreement among the Prophet’s Companions on the same matter, Analogy: applying a stated verdict to a question that carries no verdict, provided that the reasoning for this verdict applies equally to both questions.
Works of Maliki School
Sunan’s Al-Mudawwanah, rulings and statements as transmitted by Abd al-Rahmaan ibn al-Qasim; and Mukhta ar Khal l. Al-Dardr’s Al-Shar al-Kabr, with further annotations by Ibn Arafah al-Dusqi; Muhammad Al-Abdari al-Mawwq’s Al-Tj wal-Ikll; and al-ab’s shiyat Mawhib al-Jall fi Shar Mukhtaar Khall.
Works of Hanafi School
Among the best known works that explain the Hanafi school of Fiqh is Ibn Abidin’s Radd al-Muhtar ‘ala al-Durr al-Mukhtar; Mas’ud al-Kasani’s Bada’I’ al-Sana’i fi Tartib al-Shara’i; and Ibn al-Hammam’s Fath al-Qadir.
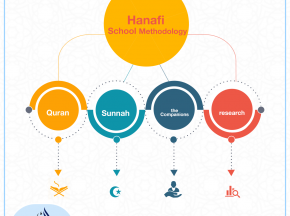
Hanafi School
Methodology: Quran, Sunnah, the Companions and research.
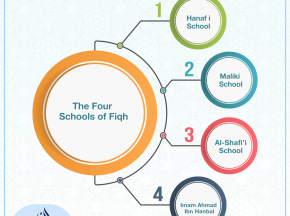
The Four Schools of Fiqh
The Four Schools of Fiqh 1: Hanafi School 2: Maliki School 3: Al-Shafi'i School 4: Imam Ahmad Ibn Hanbal
Islamic Law (Fiqh)
The subject matter of Fiqh is the description of different forms of worship and transactions and their Islamic rulings: obligation, prohibition, recommendation, reprehension and permissibly.
The fifth rukn: the pilgrimage
Hajj, or pilgrimage, means travelling to Makkah to perform this duty according to a particular manner, at a specific time and under specific conditions.
The fourth rukn: fasting in Ramadan
Fasting the days of the month of Ramadan is one of the main pillars of Islam. Anyone who denies its obligation is an apostate unbeliever.
zakat
Allah has made zakat obligatory so that it cleanses people’s hearts of greed and miserliness, provides help for the poor and the needy and gives it Allah’s blessing.
The third rukn: zakat
Zakat is one of the five pillars upon which the structure of Islam is built. Zakat is obligatory to every Muslim who owns more than its threshold.
Status of One who does not pray
Whoever does not offer prayers, denying it as an obligation, is, in effect, a disbeliever and such deliberate negligence places the one who is guilty of it outside the Islamic faith.
The second rukn: prayer
Prayer is the second most important act of worship. It makes one’s status as a Muslim clearly evident. Therefore, Islam attaches great value to it.
The importance of the declaration
it is the first rukn of Islam, providing the essence of faith and religion. It is what brings a person into the faith of Islam.
What the declaration means
‘Muhammad is Allah’s messenger’, means that we are required ‘to obey all his orders, believe whatever he stated and refrain from everything he prohibited.
What the declaration means
There is no deity worthy of being worshiped other than Allah’, means that no one may be rightly worshipped except Allah, the Glorious, the Most High.
The first rukn: the declaration
I bear witness that there is no deity worthy of being worshipped other than Allah, and I bear witness that Muhammad is Allah’s messenger.’ This declaration testifying to two important facts is the gateway to Islam.
Categories of zakat
Zakat is paid on 5 types of properties; cattle, gold and silver, commercial goods, grains and fruits and mineral resources. Each has its conditions. Those who neglect paying it are promised a painful suffering.